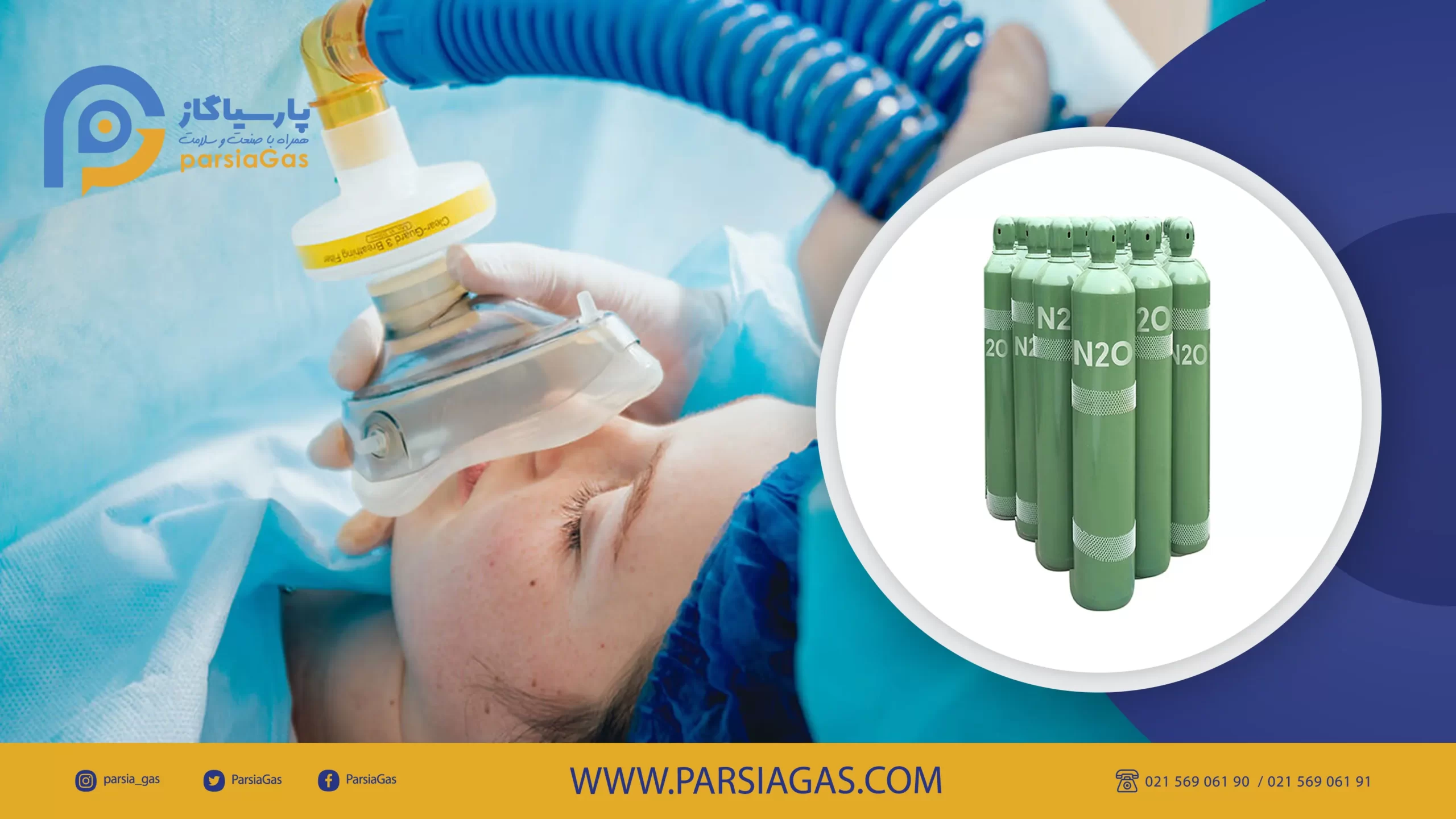
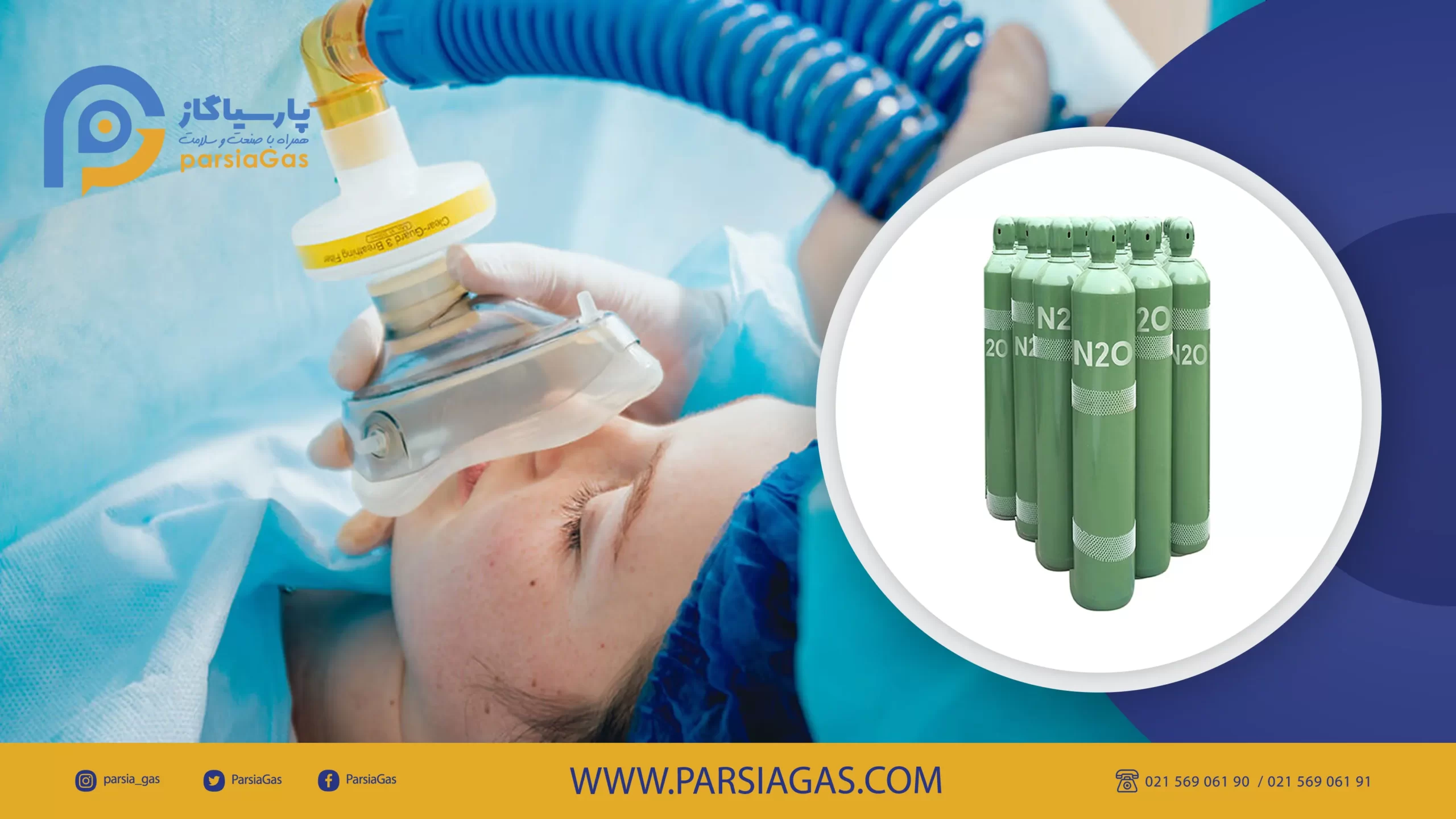
What is nitrous oxide? Gas used in anesthesia
Nitrous oxide is one of the gases used in anesthesia and operating rooms. The use of this gas improves the quality and induction of anesthesia to the patient and reduces the time required for the anesthetic to leave the patient’s body. In addition to the fact that the cost of purchasing nitrous oxide for the hospital is lower than the rest of the gases, for this reason it naturally reduces the cost of anesthesia and ultimately benefits the patient.
Nitrous oxide, also known as laughing gas, was first synthesized by Joseph Priestley in 1772. (Chemical synthesis is an activity in which a substance is made from raw materials through a chemical reaction.)
From the time of its introduction until forty years later, nitrous oxide was only used as a painkiller for teeth, but later it was used for anesthesia and analgesia in most surgical procedures, and this method continues even now.
What nitric oxide does in the body and the exact mechanism of its effect on the body is still unknown to the medical community, but its effects occur on pain centers in the brain and spinal cord. What medical science thinks of it is that nitric oxide has an effect on gamma aminobutyric acid cells and inhibits nerve cells. For this reason, it makes the patient sleepy. It is also related to the release of endogenous neurotransmitters such as narcotic peptides and serotonin, and experts in this field believe that the release of these neurotransmitters activates the descending pathways of pain and prevents pain transmission.

Contraindications to the use of nitrous oxide
- Pneumothorax
- Abdominal expansion Suspected intestinal obstruction Bullous emphysema Middle ear diseases
- Following a dive, damaged body Jaw and face injuries
- Consciousness disorder
- Poisoning
Greenhouse Effect
The environmental effects of medical nitrous oxide are very low and have only a very limited role in the production of greenhouse gases.
In fact, nitrogen oxide accounts for only 5% of the greenhouse effect, and only 1% of the total nitrogen oxide released in the atmosphere comes from medicinal uses.
It is reminded:
Parsia Gas Group produces nitrogen oxide and is ready to cooperate with hospitals all over the country. If you have any questions or would like to discuss the nitrous oxide purchasing process further, please contact us.