Air
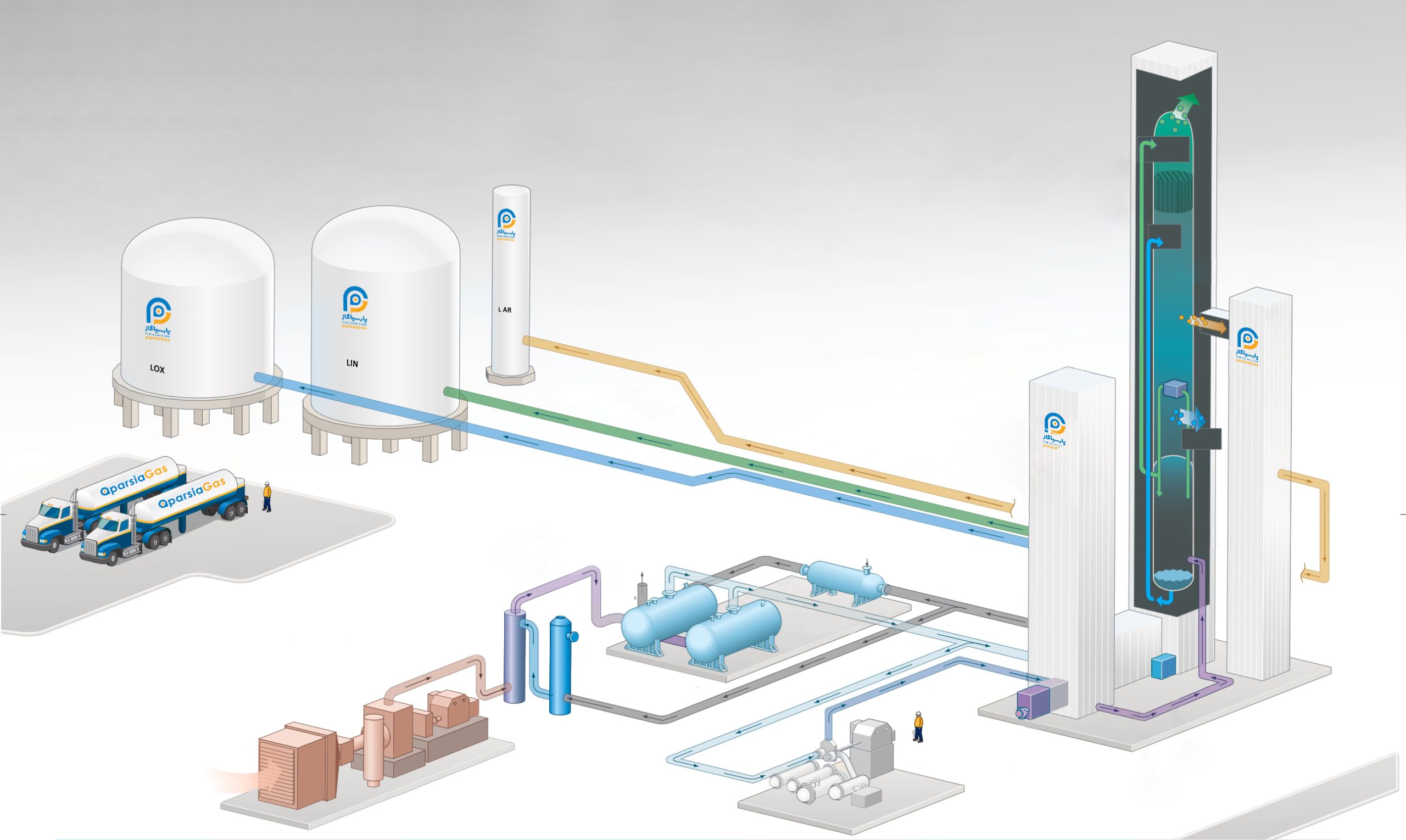
Air Separation
Air separation is the most common process used to extract the main components of atmospheric air.
Air Separation Method
In general, air separation is divided into two categories:
- Cryogenic systems
- Non-cryogenic systems
Cryogenic systems
Cryogenic systems: Cryogenic air separation technology uses the difference in the boiling points of gases to separate them.
- Distillation
- air conditioner
- heat exchange
- Air compression
- Product compression
first stage:
Ambient air is compressed using a multi-stage turbo compressor with internal coolers. Dust particles are removed using a mechanical air filter as the air enters the compressor.
second stage:
The second stage includes the removal of impurities, especially the remaining water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2). These components are removed to meet product quality specifications and before air enters the distillation section of the plant. There are two basic methods for removing water vapor and CO2.
- Reverse converters
- Molecular sieve units
Most new air separation plants use a molecular sieve pretreatment unit to remove water vapor and CO2 from the incoming air. Reverse converters for steam and CO2 removal are more cost-effective for smaller plants.
third stage:
Counterflow heat exchangers cool the process air to a temperature close to the liquid temperature.
fourth stage:
In the distillation process, trays are used to convert air into its components. The main function of the trays is to provide effective contact between the descending liquid and the rising gas.
Hence, the tray provides the basis for cooling and partial condensation of the rising gas, heating and partial vaporization of the descending liquid.
Provide.
Nitrogen exits the top of the column as a gas and oxygen exits as a liquid at the bottom of the column. A condenser at the top is used to liquefy pure nitrogen gas, and a boiler at the bottom is used to boil oxygen for greater product purity.
Argon can also be separated by withdrawing a stream in the middle of the column at the point where the concentration of argon is higher and transferring it to another column containing almost pure argon.
fifth stage:
The products are usually removed at relatively low pressures, often just over one atmosphere (absolute). In general, the lower the transfer pressure, the higher the efficiency of the separation and purification process.
Production of liquid products:
When liquid products are produced in a cryogenic air separation plant, an additional cooling unit is usually added to the basic air separation plant. This unit is called liquefier.
