Why Is Measuring Oxygen Gas Purity Important?
In medical, laboratory, and industrial fields, the quality and purity of oxygen gas play a decisive role in safety, efficiency, and system performance. Oxygen used for patients in ICUs or operating rooms must have a purity of above 99.5%. Likewise, in industrial processes such as precision welding, semiconductor manufacturing, and food industries, impure oxygen can lead to errors, equipment damage, or a reduction in final product quality.
For this reason, accurate measurement of oxygen gas purity before use or distribution is essential and cannot be overlooked. Companies like ParsiaGas, which specialize in supplying medical and industrial gases, require analytical methods that are accurate, repeatable, cost-effective, and operational to guarantee final product quality.
In this article, we thoroughly examine a classic yet highly accurate method for measuring oxygen gas purity:
the reaction of oxygen with copper metal in an ammoniacal medium.
What Is Oxygen Gas Purity and Why Must It Be Measured?
Scientific Definition of Oxygen Gas Purity
Oxygen purity refers to the percentage of oxygen present in a defined volume of a gas mixture.
For example, if a 100 cc gas sample contains 99.9 cc of pure oxygen and 0.1 cc of other gases (such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapor, or carbon monoxide), the oxygen purity is considered 99.9%.
Importance of Oxygen Purity in Different Applications
- Medical use: Oxygen must be completely free of harmful impurities to avoid risking patient health.
- High-precision industries: Even 0.1% impurity can lead to product defects or reduced process accuracy.
- Industrial welding: Impurities may cause unstable flames and significantly reduce weld quality.
Therefore, oxygen purity must be measured and verified before use or sale.
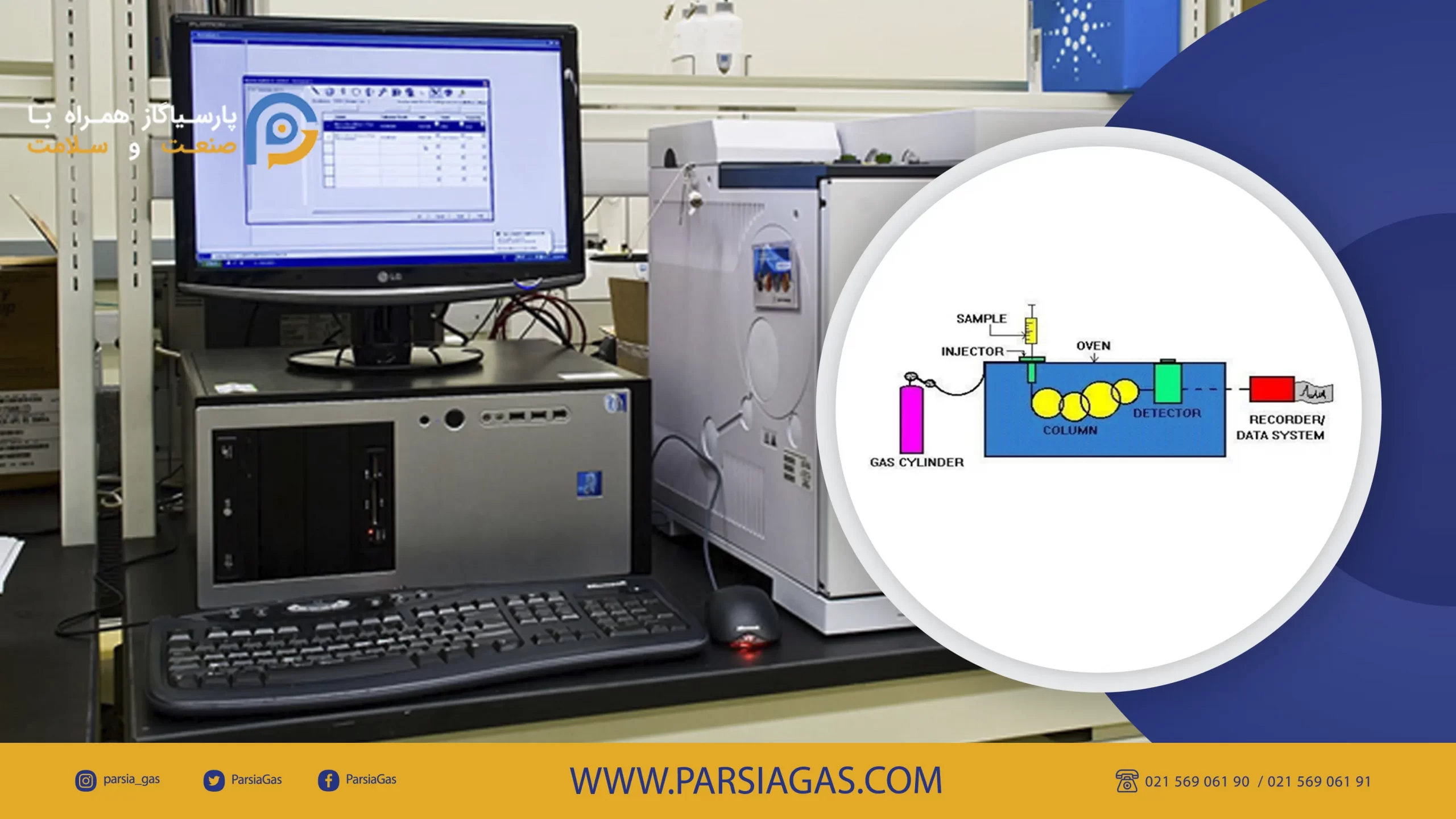
Common Methods for Determining Gas Purity
Modern Digital Methods:
- Multi-channel gas analyzers
- Gas chromatography (GC)
- Electronic oxygen purity sensors
These instruments are highly accurate and fast, but they are often expensive and require specialized maintenance and skilled operators.
Classical Chemical Methods:
When access to advanced digital instruments is limited—or when a simple yet reliable analytical approach is required—classical chemical methods are an excellent alternative.
One of the most reliable methods is explained in detail below.
Chemical Method for Determining Oxygen Purity Using Copper and Ammonia
This method is based on the chemical reaction between oxygen and metallic copper in an ammoniacal environment. Oxygen is absorbed through the reaction, and the remaining gas volume represents impurities.
By measuring:
- the initial gas volume, and
- the remaining volume after the reaction,
the oxygen purity percentage can be accurately calculated.
Advantages of This Method:
- High accuracy with excellent repeatability (error < 0.01%)
- No need for complex or expensive equipment
- Easily performed in standard laboratory conditions
- Ideal for quality control (QC) in gas production facilities such as ParsiaGas
Required Materials and Reagents
To perform this test correctly, the following materials are required:
- 550 g Ammonium Chloride (NH₄Cl)
- 1085 mL Distilled Water
- 917 mL Ammonium Hydroxide (NH₄OH)
- Standard coiled or spiral copper wire
- Burette with a two-way valve
- Glassware resistant to alkaline solutions
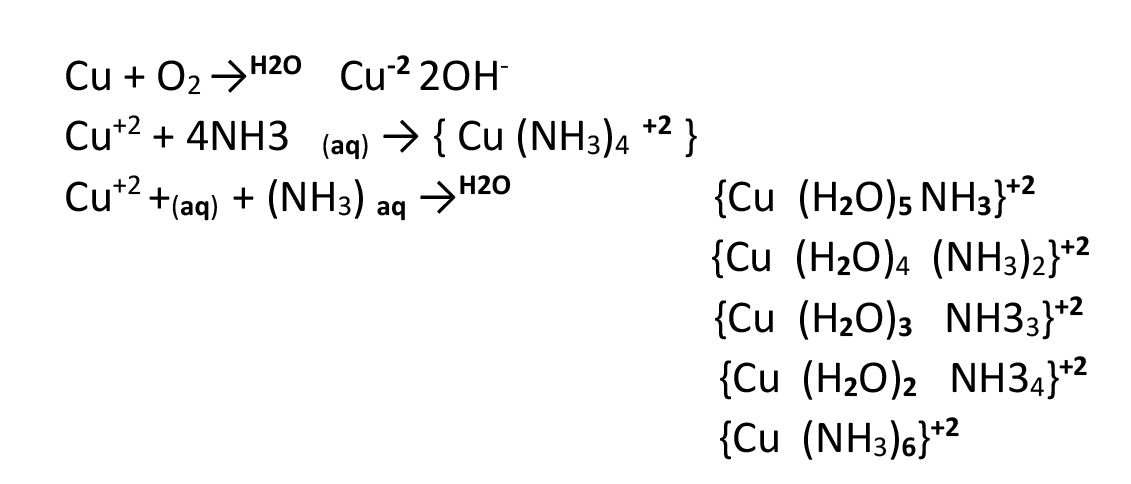
Formula for Preparing Ammoniacal Ammonium Solution
Accurate preparation of the chemical solution is critical for achieving a precise reaction with oxygen gas. This solution must be prepared by combining ammonium chloride and ammonium hydroxide in distilled water.
Required Raw Materials
| Chemical Substance | Required Amount |
|---|---|
| Ammonium Chloride (NH₄Cl) | 550 g |
| Distilled Water | 1085 mL |
| Ammonium Hydroxide (NH₄OH) | 917 mL |
Preparation Steps
- First, completely dissolve ammonium chloride in distilled water, stirring continuously until full dissolution is achieved.
- Slowly and dropwise, add ammonium hydroxide to the solution until an ammoniacal saturated solution is formed.
- Store the prepared solution in a dark or opaque glass container with a tight lid.
- Important Note: If the solution color turns dark (bluish-purple), this indicates reduced effectiveness and the solution must be replaced.
Professional Tip:
The solution should be used within 7 to 10 days to maintain optimal reactivity and accuracy.
Detailed Description of Equipment Used in the Test
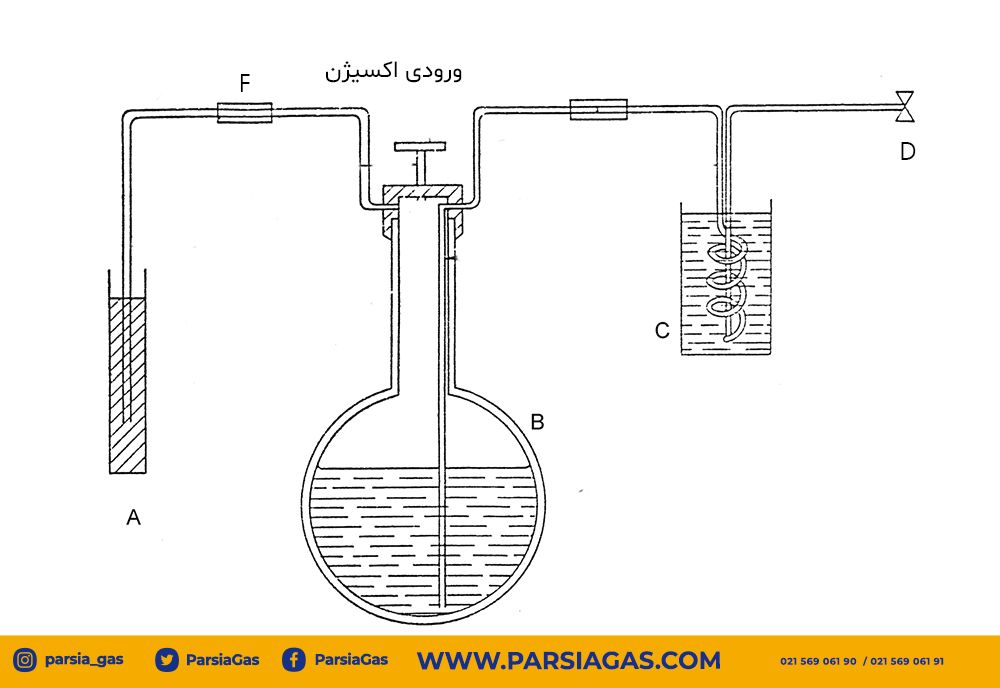
This experiment utilizes four main vessels along with auxiliary components:
1. Container A – Ammoniacal Solution Reservoir
- Contains the prepared ammoniacal solution
- Must be filled up to ¾ of its volume
- Positioned at a suitable height relative to other vessels to enable fluid flow
2. Container B – Burette with Two-Way Valve
- Oxygen gas enters the system through this vessel
- The valve allows controlled injection of a specific gas volume (e.g., 100 cc)
- The measured volume is the basis for purity calculations
3. Container C – Copper Coil Reaction Chamber
- The main reaction vessel
- Copper wires must densely and completely fill the chamber
- Must be fully sealed and leak-free
- A tight, resistant cap must be used to prevent air infiltration
4. Container D – Final Volume Control Vessel
- Collects the remaining gas after reaction (impurities)
- The gas volume here is used to calculate oxygen purity percentage
System Preparation Before Conducting the Test
Proper preparation and assembly of the system are essential.
1. Adjusting Oxygen Gas Flow
- Oxygen must enter the system at stable pressure and controlled volume
- Use a precision regulator on the gas source
2. Installing Copper Wire in Container C
- Copper wire must be clean, coiled, and free of corrosion
- Completely fill container C and tightly seal it
- Ensure all internal air is expelled before adding solution
3. Filling the System with Ammoniacal Solution
- Fill container A to three-quarters and position it appropriately
- Fill the burette (B) with ammoniacal solution
- Fill container C with the solution and place it in the reaction path
4. Verifying System Isolation
- The entire system must be airtight
- Use a soap bubble test to verify all connections
- Even minor leakage can significantly affect results
Step-by-Step Experimental Procedure
Step 1: Introducing Oxygen into the Burette
- Open the valve and introduce exactly 100 cc of oxygen gas
- Accurate volume entry is essential for correct calculations
Step 2: Transferring Gas to Container C
- Open the burette valve to allow oxygen to enter container C
- Container A may be repositioned to create positive pressure via height difference
Step 3: Oxygen Reaction with Copper in Ammoniacal Medium
- Oxygen reacts with copper to form a blue copper–ammonia complex
- The product remains in solution and does not exit the system
Step 4: Reaction Completion Time
- Allow 30 minutes for full reaction
- During this time, oxygen is gradually absorbed by the copper
Determining Impurity Volume and Final Purity Calculation
After 30 minutes:
Step 5: Reopening the Burette Valve
- Reconnect containers B and C
- Remaining gas (non-reactive impurities) returns to the burette
Step 6: Measuring Remaining Gas Volume
Example:
100 cc injected
- 97 cc absorbed
- 3 cc remaining → impurity volume
- If remaining gas is < 1 cc, purity exceeds 99%
Key Analytical Notes
- Smaller remaining volume = higher purity
- Impurities above 5% render oxygen unsuitable for medical use
- Measurement accuracy should reach 0.1 cc or better
Importance of System Isolation for Accurate Results
Any leakage or air ingress increases final volume and falsely lowers purity.
Why Isolation Is Critical
- Ambient air contains nitrogen, CO₂, and moisture
- These remain unreacted and increase impurity volume
How to Check Isolation
- Soap bubble testing on all joints
- Pressure or vacuum testing before gas injection
- Ensure container C is tightly sealed
Ensuring High Repeatability of Results
1. Constant Ambient Temperature
- Perform test at 20–25°C
- Temperature affects gas volume and pressure
2. Fresh, Standardized Reagents
- Use solution within 7–10 days
- Dark blue or purple color indicates degradation
3. Standard Copper Wire Geometry
- Reduced copper surface area leads to incomplete reaction
- Container C must be fully packed with clean copper coils
4. Precise Timing
Use a timer to ensure exact 30-minute reaction time
Physical Specifications of Copper Wire
| Parameter | Standard Value |
|---|---|
| Coil length | 1.5–2 cm |
| Coil diameter | ~0.9 cm |
| Condition | Clean, oil-free, rust-free |
| Quantity | Enough to fully fill container C |
Ammoniacal Solution Quality and Its Effect
Identifying a Proper Solution
- Light, clear blue color
- Strong ammonia odor
- No turbidity or dark discoloration
Storage Guidelines
- Use opaque, sealed containers
- Store at room temperature away from light
- Do not reuse spent solution
Chemical Method vs. Digital Analyzers
| Factor | Chemical Method (Cu + NH₃) | Digital Analyzer |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (<0.01%) | Very high (to 0.001%) |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Power required | No | Yes |
| Portability | High | Limited |
| Operator skill | Medium | High |
| Test duration | 30–45 min | Few minutes |
When digital analyzers are unavailable, this method remains a standard, economical, and reliable alternative.
Industrial and Medical Applications at ParsiaGas
1. Quality Control Before Cylinder Filling
- Verifying oxygen source purity
- Preventing contamination (N₂, CO, CO₂)
- Compliance with Ministry of Health standards
2. On-Site Testing at Customer Locations
- Builds customer confidence
- Prevents product returns and disputes
- Can be provided as quality certification
3. Periodic Quality Monitoring of Stored Cylinders
- Detects purity loss due to leakage or corrosion
- Prevents patient safety risks
- Evaluates filling and storage systems
Conclusion: Enhancing Safety and Quality Through This Method
Measuring oxygen purity is a fundamental step in ensuring safety, health, and product quality.
Although simple, the copper–ammonia method offers:
- High accuracy and excellent repeatability
- Low cost and minimal equipment
- Direct compliance with medical and industrial safety standards
By combining this method with modern techniques, ParsiaGas ensures the highest purity and reliability of supplied oxygen for even the most sensitive applications.
FAQs
1. Why is copper used in this test?
Copper reacts with oxygen in an ammoniacal medium, absorbing oxygen and separating impurities.
2. Can darkened solution still be used?
No. Dark coloration indicates degradation and inaccurate results.
3. Can this method test other gases?
No. It is specific to oxygen. Other gases require dedicated methods.
4. How does this differ from digital analyzers?
Chemical method is cheaper and portable but slower; digital analyzers are faster and more precise but expensive.
5. Does ParsiaGas offer this testing service?
Yes. ParsiaGas provides purity testing, leak checks, gas analysis, and quality certification.